Method to Convert USB flash drive to Local Disk: Insert the flash drive into the USB port of Windows (Windows 10, Windows 8, 8.1, Windows 7, Vista, XP, Windows Server 2003 and 2008) computer. Make sure that your USB drivers are updated and installed. If you are using Windows & and the latest versions, by default, your OS will keep the drivers. Cfadisk-x64-1.zip - Google Drive. Cfadisk USB Local Disk Driver allows a user to partition and format USB drives like regular hard drives. Download cfadisk local disk usb driver - cfadisk Driver. To use the driver (cfadisk.inf) you need to edit the driver file contents. You only need to change the first entry on LINE 26 of this file:%Microdrivedevdesc. Download the 64bit Hitachi Microdrive driver “cfadisk-x64-1.zip”. Download the Driver Signature Enforcement Override “dseo13b.exe” from NGHQ.com (It says it is only for up to Windows 7 but it does work on Windows 8) Download MyWCPWatermarkEditor.exe Disable secure boot on the Surface Pro.
Drive Letter hiddenWindows can be configured to hide drive letters in the Windows Explorer. Under XP the settings can be made with Microsoft TweakUI under My Computer -> Drives. Or download and execute this reg file: explorer_nodrives_0.reg
Volume has the hidden attribute
The GPT partition scheme knows a hidden attribute which prevents a partition being turned into an active storage volume. The MBR partition scheme does not have such attibutes but Microsoft fiddled in something similar: By means of the diskpart command-line tool even a MBR partition can get a hidden (and read-only) attribute. It is written into the third sector on disk (LBA2) as an rudimentrary 'Basic Data' GPT partition entry. But attributes are not in the usual place, instead they are written 32 bytes early, where the unique parition GUID belongs in a real GPT partition table. So, when a GPT drive is turned into a MBR drive and the old GPT entries at LBA2 are not clensed then there is a 50:50 chance that the MBR partition is seen as hidden and/or read-only.
Furthermore they did it all wrong: Even diskpart pretends to set the attributes per volume it reads and writes them all to the same place and so does Windows. So, on a MBR disk with multiple partitions, if you set the hidden attribute to any volume they disappear all. What a mess.
Here is how to remove the attributes:
start diskpart 'As Administrator'
list volume
The attributes are shown in the right-most column. For instance if you want to remove the hidden attribute from volume 13:
select volume 13
attribute volume clear hidden
The volume should immediately get a drive letter assigned then.
For the read-only attribute:
attribute volume clear readonly
Drive Letter Conflict with Network or Subst Drives
Since XP Network and Subst drives are no more global, they exist in the context of the user who created them only. In the context 'System' where the Mount Manager assigns drive letters such drives are not visible offhand. Therefore they are not considered by XP. If there is a network drive on the first available local letter then XP assigns it again to a new external drive. The external drive is invisible and unaccessible then until its drive letter is changed in the Disk Management (right click My Computer -> Manage -> Disk management) or by my commandline tool ReMount. But for each new drive you have to change the drive letter again and it's no solution to assign a letter again to a different external drive because XP can save exactly one assignment per letter.
So change the network drive's letter to a higher one to get the lower ones available for external drives. Or let my USB Drive Letter Manager change the letters of USB drives for you.
Microsoft is aware of this and calls it a problem. Meanwhile a hotfix is available (WindowsXP-KB297694-x86-ENU.exe) and the XP Service Pack 3 fixes the problem too.
What the SP3 did not fix is this scenario: Letters C: + D: used for local drives, E: for a USB drive. Remove the USB drive, create a network drive at E: and reattach the the USB drive again. XP with SP3 will assign E: anyway, the USB drive is 'hidden'. Another hotfix shall fix this for XP too: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/961187
This is fixed since Vista. But even Vista and Windows 7 assign a network letter to a new local drive if there is no other one available.
In general the problem persists when an external drive is attached before the user logs on. The mapping of the network drives fails when their drive letter is in use. USBDLM fixes this when configured appropriately.
New external drive not partitioned
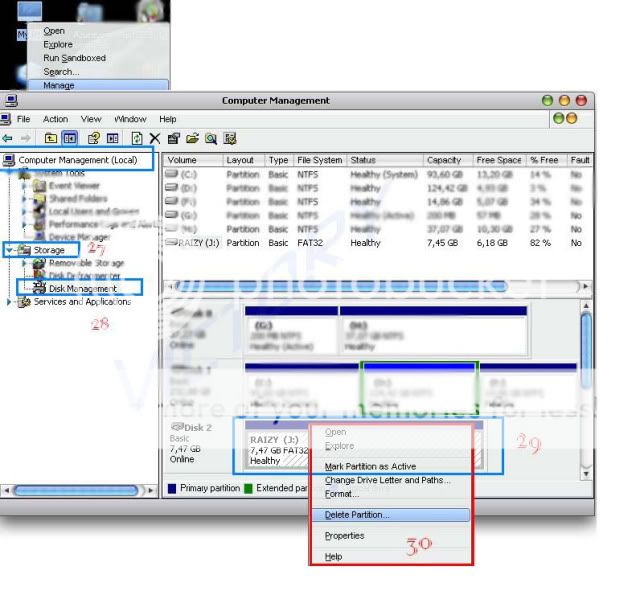
New external drives are often unformatted and unpartitioned. Partitioning can be done in the Windows Disk Management (right click My Computer -> Manage -> Disk management) or see here.
Windows Server 2003, Vista, Win7, 8, 10
Windows Server Enterprise and DataCenter Edition do not assign drive letters to new fixed drives (USB and Firewire disks are usually 'fixed'). This is up to the administrator because otherwise SAN (Storage Area Network) drives might be mounted accidentally.
This feature is called AutoMount and can be switched by means of the DiskPart tool: Open a commandprompt, enter diskpart, on the DiskPart prompt enter automount to see the current state or automount enable to enable it.
Or install my USB Drive Letter Manager which can assign a drive letter for USB and firewire harddisks without affecting other types of storage devices.
Drive encrypted
Some flash drives and external harddrives come with an encryption software. Usually you have the option to split the drive into an unencrypted and an encrypted part. The unencrypted part appears on all computers but the encrypted part becomes visible and/or accessible after you entered a password when the encryption software asks for. But of course this happens only when this software is installed on the computer you attach the drive to.
Daemon Tools V4
There are reports that a more or less failed installation of the Daemon-Tools V4 makes XP fail assigning drive letters to new drives.
It's suggested then to uninstall the tools and to delete some files in System32Drivers: sptd.sys, secdrv.sys, sptd.sys, sptdNNNN.sys (NNNN = numbers). Here are some more information:
http://www.daemon-tools.cc/dtcc/archive/index.php/t-7868.html
For the deinstallation there is sptdinst_x86.exe.
Recently there are no more reports about this issue, the problem seems to be fixed.
Filter Drivers
Filter drivers are used to manipulate the communication between soft and hardware. They are installed for instance by CD burning software (device class CDROM), backup software (device class DISK), by anti-virus software (device classes DISK, CDROM, FLOPPY and others) or by virtualization software as VMware for making USB and network devices availlable in the virtual machines (device class USB, NET).Known for causing external drive getting not mounted is the snapman filter driver installed by Acronis products, see here at terabyteunlimited.
Also after Windows updates some detail may have changed which make a causing problems.
The references to the filter drivers are found in the Registry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlClass{GUID}. GUID is an 'Global Unique Identifier', something like {4D36E967-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}.
The GUIDs mentioned above are:
| GUID_DEVCLASS_DISKDRIVE | = {4d36e967-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} |
| GUID_DEVCLASS_CDROM | = {4d36e965-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} |
| GUID_DEVCLASS_FLOPPYDISK | = {4d36e980-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} |
| GUID_DEVCLASS_USB | = {36fc9e60-c465-11cf-8056-444553540000} |
 Found filter drives can be explored under C:WindowsSystem32drivers to identify the software which has installed it.
Found filter drives can be explored under C:WindowsSystem32drivers to identify the software which has installed it.A filter driver can be deactivated by renaming the UpperFilters or LowerFilters value if it is a single entry. If not then edit the value, the Registry Editor shows each entry per line, so a single filter driver can be easily removed or their order changed if such a hint is found in the internet. To be able to restore it copy them all to somewhere before, e.g. to new MULTI_SZ value. Then restart Windows.

Digital Camera
Digital Cameras use either the USB Mass Storage Protocoll or the Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP). With the latter one there is no drive letter. For getting a drive letter a 3rd party software is required, as PTPdrive: http://www.ptpdrive.com ($29 USD).
Other 3rd party software
Anti virus, anti spyware, anti anything, personal firewalls, cd/dvd writing software, the Adobe download manager, Symantec NetBackup, usually installs a service and some drivers to get as much control as possible. Sometimes such services and drivers cause very strange effects.
To discover if a problem is caused by 3rd party software first start Windows in Safe Mode. If the problem is gone then, boot again normal. Go to Start -> Run, msconfig, Tab 'Services', check 'Hide All Microsoft Services'. Disable them all, reboot and check if the problem is gone again. If yes, then enable them one by one (reboot each time) until the problem is back again. Then you have the culprit...
If deactivating services doesn't help, try it with drivers. Start -> Run, devmgmt.msc. View -> Show hidden devices. Open in the device tree 'Non-Plug and Play Drivers'. Here you see lots of items, many from Microsoft and others. You can deactivate a driver by right clicking it an select 'Deactivate'.
If you are not sure about a driver, just enter its name at Google and you will see...
Create a system restore point before!
It is known that a flash drive or USB drive is used as a removable disk in the computer. It is mainly used to transfer data between two computer devices. In this article, you will get to know how to convert a USB flash drive to a local disk in Windows.
Reasons to convert USB Drive to a Local Disk:
Scenario 1: Sometimes it is required to use your USB drive as a local disk to install an operating system or if you are running out of memory maybe because there are large files of programs saved in your local disk. Generally, you cannot install OS on a removable disk.
Hence, if your computer is running low on internal storage space, converting USB to a local disk will help you save the storage space. Additionally, converting the external drive to local will also allow you to carry a personal computer on the go. So, you can just plug and play whenever it is required.
Scenario 2: Generally, Windows only supports multiple partitions for hard disk drives that are identified as local. The only way you can create a partition on a USB drive is by converting the USB drive to a local disk.
Since, recently most of the storage drives provide storage space of 1TB and above, converting USB to local disk will allow you to create partitions. A better way to organize your vast amounts of data.
There are various ways to convert a USB flash drive as the local disk; here I am listing one of the best and most convenient methods of converting USB to a local drive:
Note: Before performing these steps make sure you create a backup of your flash drive data else, you may lose your files. In case that happens, immediately stop using the drive and recover lost files from the flash drive using Remo Recover Software.
Method to Convert USB flash drive to Local Disk:
- Insert the flash drive into the USB port of Windows (Windows 10, Windows 8, 8.1, Windows 7, Vista, XP, Windows Server 2003 and 2008) computer.
- Make sure that your USB drivers are updated and installed. If you are using Windows & and the latest versions, by default, your OS will keep the drivers updated.
- Sometimes you may need to format the drive to avoid any kind of errors. But don't forget to create a backup before you format the USB drive.
- Unfortunately, if you forgot to create a backup of any of the files and lost them in formatting, you can use an efficient flash drive recovery software to restore lost files...
- Then you have to download the USB_LocalDisk.zip and extract it.
- From the USB LocalDisk folder right click on cfadisk.inf and open it using Notepad or Notepad ++ or text editor
- Then go to line 26 of the .inf file

Cfadisk Usb Driver X64 Download
Note: We are going to edit the section named “device_instance_id_goes_here”. It is better to keep this file open.
- From the desktop, click Start > Run and then type “devmgmt.msc” and press OK to open device manager.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as an administrator
- Find your USB stick under the Disk drives tab and right-click then select Properties.
- Then go to Hardware Tab and select the Removable disk. Click on Properties.
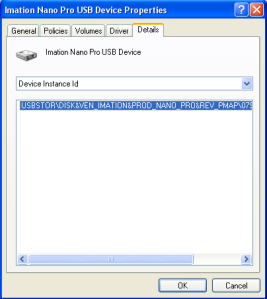
- Then open the Details tab and select Device description. Click on the Device instance path from the list.
- Select the Value and take the help of the Ctrl + C key combination to copy the Device instance path.
- Go ahead and again open the .inffile i.e. cfadisk. Here you will insert the drive code and Save the file.
- Locate the text which says “device_instance_id_goes_here” should be around line 26. Then paste the drive code you have using the paste option or by Ctrl + V.
- Hit Save button (So now we have created an updated driver for the device, so it will now read as a Local Disk. Now we just need to update the driver itself)
- Go to Start > and type Disk Management. Under disk management select the tab below saying Removable Disk. Right-click on it and click on Properties.
- Go to the Driver tab and select on “Update Driver” option and select Browse for Driver Software on our computer. Then click on Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
- Click on Have disk>Next> Browse.
- Browse to your recently edited cfadisk.inf file location under USB_LocalDisk folder. Then click on Open.
- Hit OK>Next and then click on Yes on the below-mentioned warning.
- In the next prompt of the Windows Security window click on Install this driver software anyway.
- Once it shows Windows has successfully updated your driver software you can click on Close.
With these steps, you can easily convert your flash drive into a local disk. Again open Disk Management and now you will see the removable disk as a local drive.
However, once you are done with the above steps, you can not only install the operating system on the USB drive but it will also help you when your system is running out of memory. Make sure your USB has sufficient memory before performing these options.
You can partition the USB Flash Drive now in Windows 10 using Disk Management
NOTE: If you have some data stored in the Drive then take a backup before you perform the following steps.
Steps to follow:
- Insert the thumb drive into the USB port of the Windows Computer.
- Open File Explorer and right-click on the USB Drive and click on Format
- Then in the next window change the File System type from exFAT to NTFS.
- Give a name to the Volume label and Click on Start.
- Once the format is complete, click on Close.
- Click on the Windows button and go to Disk Management.
- In the Disk Management window click on the name of the drive that is the volume name. Then right-click on it and select Shrink Volume.
Cfadisk 64
- Then in the next window, you can choose the volume size and click on Shrink.
Cfadisk Usb Driver X64 Windows 10
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select New Simple Volume and click on Next. Give a name to the new volume and again click Next > Finish.